Shedding Light on Solar: How Solar Panels Drive Development and Sustainability
Shedding Light on Solar: How Solar Panels Drive Development and Sustainability
Shedding Light on Solar: How Solar Panels Drive Development and Sustainability:
As the world continues to seek sustainable energy solutions, solar power has emerged as a frontrunner in the quest for a cleaner and more efficient future. In this article, we shed light on how solar panels are driving both development and sustainability.
Solar power harnesses the energy of the sun to generate electricity, providing a renewable and reliable source of power. It not only reduces our reliance on fossil fuels but also helps combat climate change by reducing carbon emissions. The rise of solar energy has paved the way for innovative technologies and created new job opportunities in the renewable energy sector.
From residential rooftops to massive solar farms, solar panels are becoming increasingly common sights worldwide. Their versatility and scalability make them suitable for various applications, whether it's powering individual homes, supplying electricity to entire communities, or even fuelling electric vehicles.
This article explores the numerous advantages of solar power, including its environmental benefits, economic potential, and role in fostering sustainable development. By shedding light on solar, we hope to inspire a greater understanding and appreciation for this clean and abundant source of energy.
The environmental benefits of solar energy:
Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity using a process called the photovoltaic effect. The panels are made up of individual solar cells, which are typically made from silicon, that absorb photons from the sun and release electrons. These electrons are then captured and turned into usable electricity.
The efficiency of solar panels has improved significantly over the years, with modern panels able to convert more sunlight into electricity than ever before. This means that even in areas with less intense sunlight, solar panels can still generate a significant amount of power.
Solar panels are designed to be durable and require minimal maintenance. They can last for several decades, making them a cost-effective investment in the long run. Additionally, advancements in solar panel technology have made them more aesthetically pleasing, allowing for seamless integration into various architectural designs.
Solar panels can be installed on rooftops, open fields, or even floating on water bodies. The choice of installation location depends on factors such as available space, sunlight exposure, and local regulations. Regardless of the installation site, solar panels have proven to be a reliable and efficient source of clean energy.
Solar energy and its impact on sustainable development:
Solar energy offers numerous environmental benefits that make it a compelling choice for sustainable power generation. One of the most significant advantages is its role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, solar power does not release harmful pollutants or carbon dioxide when generating electricity. This helps combat climate change and improve air quality.
In addition to reducing carbon emissions, solar energy also conserves water resources. Traditional power plants, particularly those fueled by coal or natural gas, require vast amounts of water for cooling purposes. Solar panels, on the other hand, do not require water for their operation, making them a water-efficient alternative.
Another environmental benefit of solar energy is the preservation of natural habitats. Extracting and burning fossil fuels often leads to habitat destruction and the disruption of ecosystems. By transitioning to solar power, we can minimize our impact on the environment and protect precious wildlife habitats.
Furthermore, solar energy is a renewable and abundant resource. The sun provides an infinite supply of energy, ensuring that solar power remains sustainable and accessible for future generations. By harnessing this clean and renewable energy source, we can reduce our dependence on finite fossil fuels and create a more sustainable future.
Case studies showcasing successful solar energy projects:
Solar energy plays a crucial role in fostering sustainable development on both a local and global scale. By providing access to clean and affordable electricity, solar power can improve the quality of life in communities around the world.
In many developing regions, access to electricity is limited or unreliable. Solar panels offer a decentralized and independent power source that can bring electricity to remote areas. This enables communities to access essential services such as lighting, healthcare, education, and communication, empowering them to thrive and grow.
Solar energy also has economic benefits that contribute to sustainable development. The installation and maintenance of solar panels create job opportunities in the renewable energy sector. This sector has seen significant growth in recent years, and the demand for skilled professionals continues to rise. By investing in solar power, countries can stimulate their economies and create a more resilient and sustainable workforce.
Furthermore, solar energy can reduce energy costs for individuals and businesses. As the cost of solar panels continues to decrease, more people are turning to solar power as a cost-effective alternative to traditional electricity sources. This not only reduces the financial burden on households but also improves the competitiveness of businesses, particularly those in energy-intensive industries.
Overall, solar energy provides a pathway to sustainable development by addressing energy poverty, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, creating job opportunities, and driving economic growth.
Government incentives and policies promoting solar energy adoption
Numerous successful solar energy projects have demonstrated the positive impact of solar power on development and sustainability. These case studies highlight the versatility and effectiveness of solar panels in various settings.
One such example is the SolarCity project in the United States. SolarCity, now a part of Tesla, aims to make solar energy accessible and affordable to homeowners. Through innovative financing models, SolarCity offers solar panel installation with no upfront costs, allowing homeowners to pay for the system through monthly payments. This approach has made solar power more accessible to a wider audience, driving the adoption of renewable energy at the residential level.
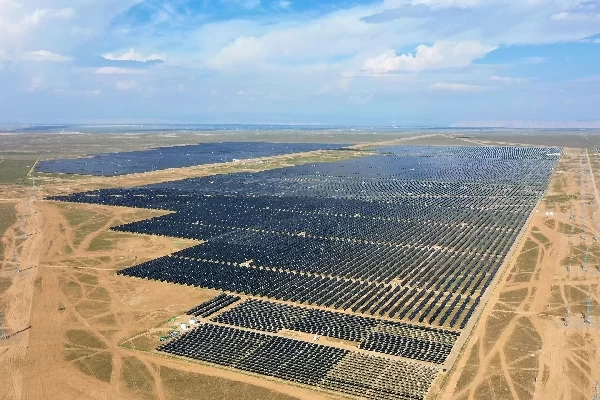
In India, the Kamuthi Solar Power Project stands as a testament to the scalability of solar energy. Located in Tamil Nadu, this solar farm covers an area of 2,500 acres and has a capacity of 648 megawatts. It is one of the largest solar power plants in the world and provides electricity to over 150,000 homes. The project showcases the potential of large-scale solar farms to meet the energy needs of entire communities and reduce reliance on traditional power sources.
Another notable case study is the Solar Impulse project, which aimed to demonstrate the capabilities of solar-powered flight. The Solar Impulse 2, a solar-powered aircraft, completed a historic around-the-world flight in 2016, relying solely on the power of the sun. The project showcased the reliability and potential of solar energy in transportation, paving the way for cleaner and more sustainable aviation in the future.
These case studies highlight the diverse applications of solar energy and its ability to drive sustainable development in different sectors. By learning from these successful projects, we can continue to unlock the full potential of solar power.
Overcoming challenges in implementing solar energy projects:
Government incentives and policies play a crucial role in driving the adoption of solar energy. Many countries around the world have implemented measures to encourage the installation of solar panels and promote the growth of the renewable energy sector.
One common incentive is the provision of financial incentives, such as tax credits or rebates, for individuals and businesses that invest in solar power. These incentives help offset the initial costs of installation and make solar panels more affordable and attractive to potential adopters. In some cases, governments also offer feed-in tariffs, which allow solar panel owners to sell excess electricity back to the grid at a favorable rate.
Additionally, governments can implement regulations and standards that require a certain percentage of energy to come from renewable sources, including solar power. These policies create a market demand for solar energy and encourage investment in renewable projects. By setting ambitious renewable energy targets, governments can drive the transition to cleaner and more sustainable power generation.
Government support is particularly crucial for developing countries, where the upfront costs of solar panel installation may be prohibitive for individuals and businesses. Through international collaborations and funding, governments can provide financial assistance and technical expertise to help these countries adopt solar power and achieve their sustainable development goals.
The future of solar energy and its potential for growth:
While solar energy offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential. One such challenge is the intermittency of solar power. Solar panels generate electricity only when exposed to sunlight, which means that energy storage systems are required to ensure a consistent power supply during periods of low sunlight or at night.
Advancements in battery storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, have made significant progress in addressing this challenge. These batteries can store excess energy generated during the day and release it during times of low or no sunlight. With further research and development, energy storage systems can become more efficient and affordable, enabling the widespread adoption of solar power.
Another challenge is the integration of solar power into existing energy grids. Solar energy is typically generated at the point of consumption, such as individual homes or businesses. This decentralized nature of solar power can pose challenges for grid management and stability. However, smart grid technologies and advanced grid management systems can help overcome these challenges by efficiently balancing supply and demand and integrating renewable energy sources into the grid.
Furthermore, the upfront costs of solar panel installation can be a barrier for many individuals and businesses. While the long-term cost savings of solar energy are significant, the initial investment can be prohibitive. Governments and financial institutions can play a crucial role in addressing this challenge by providing financial incentives, low-interest loans, and innovative financing models that make solar power more accessible and affordable.
Tips for residential and commercial solar panel installation:
The future of solar energy looks promising, with significant potential for growth and innovation. As technological advancements continue, solar panels are becoming more efficient, cost-effective, and aesthetically pleasing. This makes them an increasingly attractive option for residential and commercial applications.
One area of innovation is the development of solar panels with increased efficiency and durability. Researchers are exploring new materials and designs that can enhance the performance of solar cells and improve their ability to capture sunlight. Additionally, advancements in nanotechnology and thin-film solar panels hold the potential to make solar energy more accessible by reducing the cost of production and installation.
The integration of solar power with other renewable energy sources is another area of interest. Hybrid systems that combine solar panels with wind turbines or energy storage systems can provide a more reliable and consistent power supply. This integrated approach maximizes the benefits of different renewable energy sources and improves overall energy efficiency.
The future of solar energy also lies in the development of smart cities and sustainable infrastructure. Solar panels can be integrated into the design of buildings, roads, and public spaces, transforming them into energy-generating assets. This concept, known as building-integrated photovoltaics, allows for the seamless integration of solar power into urban environments and reduces the need for separate solar installations.
Furthermore, solar energy has the potential to revolutionize transportation. Solar-powered electric vehicles (EVs) can help reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable mobility. Advancements in EV battery technology, combined with solar charging stations, can make solar-powered transportation a viable and environmentally friendly option.
Conclusion: Embracing solar energy for a sustainable future:
Installing solar panels at the residential or commercial level requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some tips to ensure a successful installation:
1. Conduct a solar feasibility assessment: Before installing solar panels, assess the suitability of your location in terms of available sunlight, shading, and roof orientation. A professional solar installer can help determine the optimal design and capacity of the system.
2. Choose reputable solar panel manufacturers and installers: Look for well-established companies with a track record of quality and customer satisfaction. Read reviews and seek recommendations to ensure you're working with reliable professionals.
3. Consider your energy needs and goals: Determine your energy consumption patterns and set realistic goals for solar power generation. This will help determine the size and capacity of the solar panel system required.
4. Understand financial incentives and financing options: Research the available financial incentives, tax credits, and financing options in your area. Take advantage of government programs or seek financing options that make solar power more affordable.
5. Regularly maintain and monitor your solar panel system: Keep your solar panels clean and free from debris to ensure optimal performance. Monitor your system's energy production and address any issues promptly to maximize energy generation.
6. Educate yourself and your community: Share your experience with solar power and educate others about its benefits. By raising awareness and encouraging adoption, you can contribute to a more sustainable future.
Previous:Tashkent Launches 60MW Solar Production Line, Leading Uzbekistan's Renewable Energy Revolution
Next:The main differences between N-type and P-type monocrystalline silicon wafers for solar photovoltaic
cut cell to half, 1/3 1/4 1/5 1/6 1/7 1/8
Non Destructive Cutting Machine Thermal Laser Separation Cutting Machine
Solar Cell IV Test before Tabbing
solar strings busbar welding after layup
Market Research Industry Learning